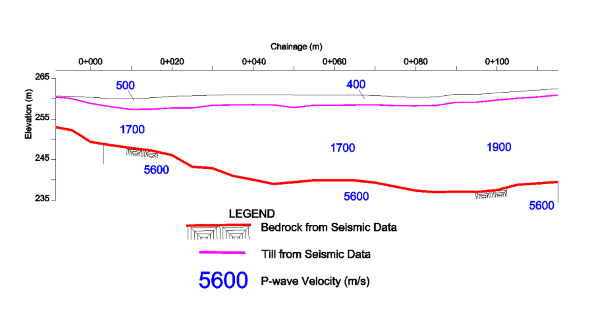
The seismic refraction method involves measuring the shortest time required for an induced seismic pulse to travel from the source location to a series of receivers. From this travel time data, seismic velocities and layer depths can be calculated.
Seismic refraction remains the preferred method for accurately mapping the depth to competent bedrock under most conditions.
Typical applications of seismic refraction include:
- Bedrock profiling and locating of faults and fracture zones;
- Calculating the modulus of elasticity of the various layers;
- Determining the depth to the water table;
- Determining the thickness of overburden layers;
- Identifying sub-vertical geological contacts.
For more information, please contact our Ground Survey Team.

Marine Seismic Surveys
The seismic refraction method extends seamlessly into marine environments and across rapids.
The Marine chapter of our website contains more information on seismic surveys for mapping bedrock beneath bodies of water.
